Beyond the "Co-Pilots" - Six Part AI-driven Security Framework
The HAEGID Framework - a six-part AI framework to decode how AI impacts cybersecurity
Hello Cyber Builders 🖖
I recently examined how AI is used across 12 cybersecurity platforms, focusing on real examples from vendor product releases over the past 2 years. You’ll find all the resources linked below.
This series generated passionate questions and remarks. Some of you told me, “I will never delegate my security operations to an AI.” Others were excited about delegating boring research and reporting to focus on more valuable work.
No matter your view, cybersecurity is a grind. Alerts pile up, tools don’t always work together, skilled people are hard to find, and threats keep changing. Many of you deal with this daily.
Our community needs a straightforward way to see how AI helps both products and day-to-day work. We have to look past vendor claims like, “My new release includes the best AI feature!” It’s also crucial for Cyber Builders to explain to customers how they leverage AI and why.
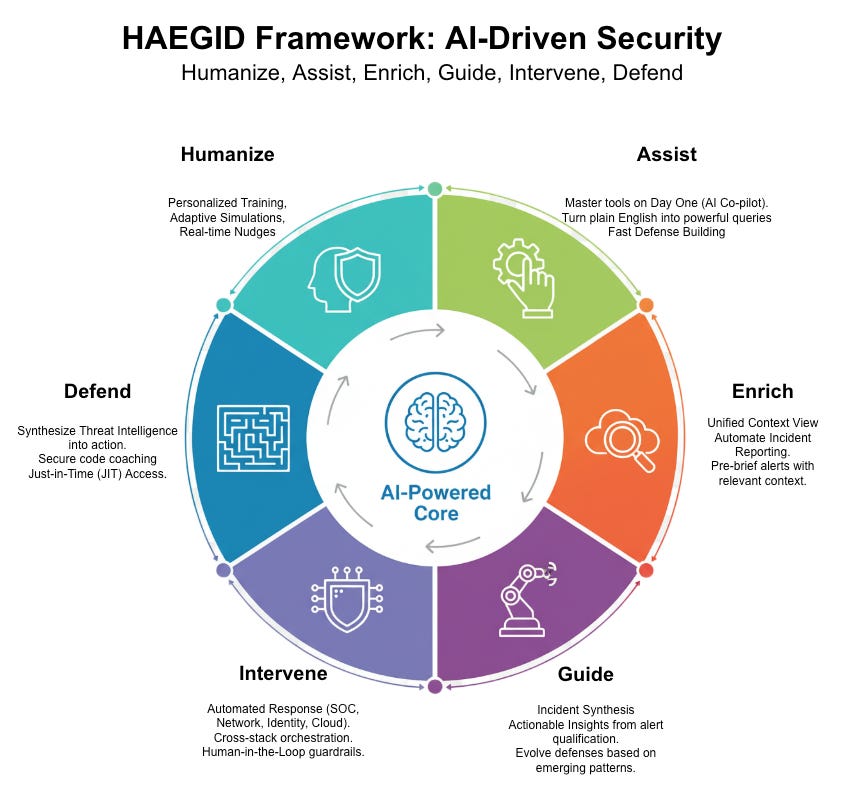
To address this, I have developed a unified framework for AI-driven security: HAEGID.
HAEGID stands for Humanize, Assist, Enrich, Guide, Intervene, and Defend. Unlike other models, it uniquely connects real security team challenges with targeted AI solutions, emphasizing practical, human-centered collaboration from the ground up.
Humanize: Use tailored training and real-time prompts to empower your team’s defenses.
Assist: Help analysts become faster and more accurate with their tools from the start.
Enrich: Automatically gather context for alerts so analysts see the full picture immediately.
Guide: Turn noisy data into clear incidents, steering teams toward correct action.
Intervene: Enable rapid, coordinated responses across all security tools.
Defend: Proactively hunt for threats and strengthen your defenses early.
In the following sections, we will explore each pillar with practical use cases you can implement in your environment. HAEGID offers a direct, actionable approach to align AI features with measurable improvements in security operations, guiding you from initial interest to reliable, value-driven AI use cases.
We will begin by examining the first pillar of HAEGID, Humanize, and review relevant examples that demonstrate its immediate potential.
Note: HAEGID is pronounced “HEY-GID.” 😅
H - Humanize: Fortifying Your Human Layer
For years, people have been labeled the weakest link in security. I disagree. Your team is your greatest asset and first line of defense when properly empowered. Rather than relying on generic training, Generative AI enables tailored training, simulation, and guidance within daily workflows.
AI personalizes and continuously adapts human-oriented security activities. By contextualizing experience, it turns employees into the first line of defense by integrating security training and guidance into daily workflows.
Deliver Hyper-Personalized Security Training
Effective training is relevant and practical. GenAI enables the delivery of hyper-personalized lessons tailored to each role’s daily responsibilities. For example, a finance analyst receives training on identifying wire fraud, while a cloud engineer receives guidance on securing their specific infrastructure. This targeted approach drives meaningful behavior change.
Run Realistic and Adaptive Attack Simulations
Traditional phishing simulations are becoming obsolete as attackers adopt more sophisticated tactics. GenAI allows you to create realistic simulations that mirror current threats, including deepfake voice calls for high-risk roles. This approach identifies those most at risk and enables targeted, individualized coaching.
Provide Continuous Reinforcement with Real-Time Nudges
Addressing risky behavior is most effective when done in real time. GenAI can provide timely, relevant guidance as needed. For instance, if an employee attempts to upload sensitive data, a clear message can explain the risk, helping prevent errors and reinforce positive security habits.
A - Assist: Empowering Your Analysts, Every Step of the Way
You probably already know this part of HAEGID. Generative AI delivers assistance by acting as a co-pilot for your security team. SOC analysts are faster, co-pilots level up your junior members, and reduce the friction of hand-offs between teams.
AI acts as an on-demand co-pilot, lowering barriers to complex tasks and automating tedious work for your team.
Master Your Tools on Day One
New security tools often introduce initial complexity, reducing productivity. GenAI helps eliminate this barrier.
Imagine your newest analyst asking a tool directly, “How do I trace this alert from the SIEM all the way to the EDR?”
Instead of searching through documentation, analysts receive step-by-step guidance within their workflow. This contextual training accelerates onboarding and reduces escalations to senior staff.
Turn Plain English into Powerful Queries
Query languages should not hinder analysis. Traditionally, only those proficient in specialized syntax could ask complex questions. GenAI serves as a universal translator.
Now, anyone on your team can ask, “Show me all failed logins for Jane Doe from outside the US in the last 24 hours.”
The AI generates the correct query and returns results, enabling junior analysts to contribute valuable insights from their first week.
Guide the Next Best Action
When a critical alert occurs, hesitation can create risk. GenAI acts as a real-time guide, recommending the best course of action based on the alert’s context.
It might suggest, “Check for recent process creation on the host,” or “Quarantine the device if indicators of lateral movement appear.”
These suggestions are tailored to your environment and informed by existing playbooks, ensuring higher-quality investigations.
You can begin by adding a “recommended actions” panel to your triage view, providing your team with a concise list of steps and one-click links.
Don’t automate trust.
Keep a human in the loop.
The journey should be gradual.
Start with AI suggesting actions, then graduate to one-click execution, and finally, to supervised auto-execution for your lowest-risk, highest-confidence tasks.
E - Enrich: Getting the Full Picture, Instantly
Most security alerts require context, not additional noise. The “Enrich” use case transforms isolated signals into actionable insights, providing analysts with a comprehensive view to support faster, more informed decisions.
AI eliminates the need for analysts to pivot between tools to understand an alert manually. It aggregates and synthesizes relevant context, turning a raw event into an actionable story. Note that if the underlying data isn’t a bit normalized (a problem the industry hasn’t solved in 20 years of SIEM), the AI’s “unified view” will be flawed
Reclaim Your Time from Incident Reporting
Reporting after every major incident is a significant burden. GenAI can automate the drafting of post-incident reports, executive summaries, and regulator-ready narratives.
By extracting key details directly from investigation data, GenAI assembles a coherent first draft, links relevant evidence, and suggests remediation actions. This approach saves significant time and ensures consistent reporting quality.
End the Swivel-Chair Investigation
When a detection occurs, analysts often need to gather context from multiple sources, such as user roles, asset criticality, known vulnerabilities, and threat intelligence. This process is time-consuming and inefficient.
GenAI can consolidate this information by integrating with existing tools and data sources, presenting all relevant context in a unified view alongside the alert. This enables faster triage, improved decision-making, and reduced frustration.
Start small.
Limit your initial scope to two or three data sources per detection family.
Always capture the data’s provenance so you know where each piece of information came from.
G - Guide: Making Sense of the Chaos
While SIEMs generate numerous alerts, synthesis is essential. The “Guide” use case focuses on consolidating noisy events into a coherent incident narrative to guide teams to accurate conclusions.
AI moves beyond presenting data to actively interpreting it. It acts as a synthesis engine, connecting the dots among thousands of low-signal, disparate events to identify a single, coherent incident and guide the analyst toward the most effective course of action.
Let Your Defenses Evolve with the Adversary
Effective defenses are adaptive. Rather than relying on manual trend analysis, GenAI monitors emerging patterns and proposes new detections or response playbooks.
For example, GenAI can identify an increase in a specific TTP and suggest a new detection rule, complete with tuning options and a recommended response flow.
This allows your defenses to evolve in near real-time, driven by the threats you’re actually facing.
From Alert Fatigue to Actionable Insight
A high volume of low-signal alerts can quickly overwhelm a SOC. Alert qualification addresses this by providing analysts with a single, synthesized incident summary instead of multiple confusing alerts.
This summary should provide a clear timeline, the incident scope, potential impact, a list of affected assets, and the likely root cause, all with a stated confidence level.
It’s the difference between showing someone a pile of bricks and showing them a house.
This approach significantly reduces alert fatigue and enables faster, more confident triage.
I - Intervene: Taking Decisive Action
While assistance is valuable, decisive intervention is essential for incident resolution. In the “Intervene” phase, Generative AI evolves from a co-pilot to an agent capable of orchestrating multi-step responses across the security stack.
The key is to do this safely, with human-in-the-loop guardrails from the start.
AI enables an accurate machine-speed response. It moves from a passive co-pilot to an active agent that can take direct, decisive action across your entire security stack, moving beyond rigid, pre-defined playbooks to execute dynamic interventions.
An intelligent GenAI agent should detect threats, determine the best response, develop a plan, and execute it. This capability should extend beyond the SOC to the entire environment.
Here’s how it breaks down by domain:
In the SOC, this means automating manual, repetitive tasks for incident responders. For example, AI can isolate compromised hosts, block malicious domains, expire user sessions, and open tickets with asset owners within seconds of an alert. A practical starting point is piloting automated blocking of known malicious domains.
For Network Security: The AI can push immediate updates to your security infrastructure. It could add a malicious domain to a DNS sinkhole, update a SASE policy to block a new C2 channel, or even microsegment a network zone where suspicious activity is detected to prevent lateral movement.
Across Identity & Access: This is about responding to identity-based threats in real time. The AI can enforce conditional access policies, trigger a step-up authentication challenge for a user exhibiting risky behavior, or suspend a compromised account entirely. It can also enable true just-in-time (JIT) access, granting temporary elevated privileges for a specific task and automatically revoking them afterward.
For Data Security: When a DLP policy fires, the AI can take immediate containment actions. It could quarantine a sensitive file, revoke all external sharing links, and notify the data owner with a list of remediation options, turning a potential data breach into a contained event.
In cloud environments, rapid response is essential. AI can automatically quarantine suspicious workloads, apply restrictive security policies, rotate compromised credentials, or roll back risky infrastructure changes. A valuable initial use case is detecting newly public S3 buckets and automatically applying private ACLs.
To ensure safety, establish clear rules of engagement.
Define risk tiers to determine which actions can be automated and which require human approval.
Record the AI’s intent and approval, and regularly test rollback plans.
The objective is to achieve measurable outcomes such as reduced MTTR, fewer escalations, and time saved per incident.
D - Defend: Proactively Outsmarting Attackers
Many security programs have been reactive for too long. Proactive teams succeed by identifying early signals, anticipating adversary actions, and strengthening defenses before attacks occur. Generative AI enables this proactive approach.
AI enables a shift in the security paradigm from reactive to proactive. It allows your team to anticipate and neutralize threats before they can cause damage by identifying emerging patterns and hardening defenses earlier in the attack lifecycle.
Automate Threat Hunting
Manual threat hunting cannot keep pace with the current volume of intelligence and attacks. Automating this process with GenAI allows the AI to ingest data, cluster attacker TTPs, and automatically initiate targeted threat hunts.
When a suspicious pattern emerges, GenAI can initiate investigations on autopilot, correlate evidence, score risk, and surface only high-confidence leads to your team.
Build Security into Your Code
Scaling security requires a shift-left approach, and GenAI can support developers by integrating into the CI/CD pipeline. It acts as a real-time security coach, suggesting secure coding patterns, flagging vulnerabilities, and proposing specific fixes with code diffs.
This integration embeds security into the developer’s workflow, reducing vulnerabilities and minimizing the need for manual security code reviews.
Move to a Model of Dynamic, Just-in-Time Access
Static access policies and standing privileges are risky, as they become outdated and increase the potential impact of a compromise.
GenAI enables a more dynamic and secure approach. It can generate context-aware, fine-grained access policies on the fly, granting a user time-boxed, task-scoped access to a specific resource and then revoking it when the task is complete.
This is the essence of Zero Trust, and it dramatically reduces your attack surface.
Conclusion
AI is no longer a buzzword in cybersecurity—it’s an operational necessity.
It promises that by focusing on practical automation, continuous investigation, and human-centered collaboration, security teams can stay ahead of attackers and turn today’s challenges into tomorrow’s strengths.
The HAEGID framework offers a compelling visionary roadmap, recognizing that ‘Chatbots’ (Assist) are merely the starting point.
The leap from “Assist” to “Intervene” is massive. The article glosses over the “Trust Gap.” Cyber Builders might trust an AI to write a SQL query (Assist), but trusting it to “quarantine a sensitive file” or “revoke access” autonomously is a different universe of risk. The HAEGID framework implies this is a linear progression, but operationally, it’s a quantum leap.
What would be the criticisms of this framework? Let’s do my own critique. HAEGID probably takes an overly optimistic stance on data integration and downplays the operational risks associated with 'Intervene’ (automated actions); or it presumes a pristine data environment, which is seldom the case, and overlooks the ‘explainability’ crisis that emerges when AI agents begin making decisions affecting human employees.
I’ll be happy to understand how you can use the HAEGID framework to assess this promise. Next time you face a vendor claim, will it help? DM me to tell.